15-Jul-2025
New insights into the #jetStream make better #climate predictions possible
Researchers uncover how climate change impacts the “weather motor”
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1091239 #science #climateCatastrophe
15-Jul-2025
New insights into the #jetStream make better #climate predictions possible
Researchers uncover how climate change impacts the “weather motor”
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1091239 #science #climateCatastrophe
Bonus Photo of the Day 16th July 2025.
G-LAKJ, British Aerospace Jetstream 3102, Lakeside NorthWest, at Liverpool Speke, 17th September 1993.
#Liverpool #Speke #LPL #EGGP #BritishAerospace #Jetstream #J31 #LakesideNorthWest
#AvGeek #aviation #planespotting #photography
#EddyDrivenJet unter Beobachtung: Wie wirkt sich der #Klimawandel auf den „Wettermotor“ aus?
https://www.l-iz.de/bildung/forschung/2025/07/eddy-driven-jet-unter-beobachtung-klimawandel-wettermotor-629483
#Leipzig #Uni #Jetstream #Meteorologie
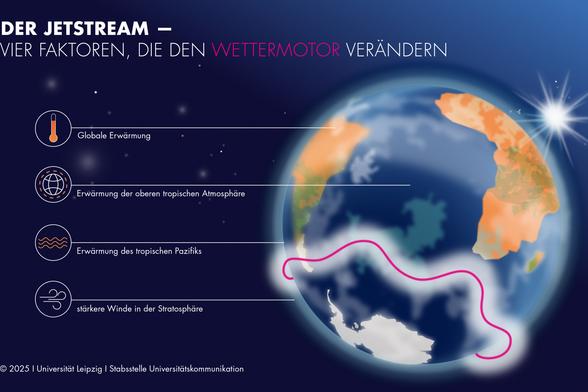
"50% of the observed shift in the Southern Hemisphere's #jetstream is directly attributable to #globalwarming . The other half is caused by a combination of other climate-related changes. These include the warming of the upper tropical atmosphere, the strengthening of the winds in the stratosphere and the warming of the tropical Pacific. While some of these factors are also influenced by anthropogenic #climateChange , others are more difficult to attribute."
https://phys.org/news/2025-07-insights-jet-stream-climate.html
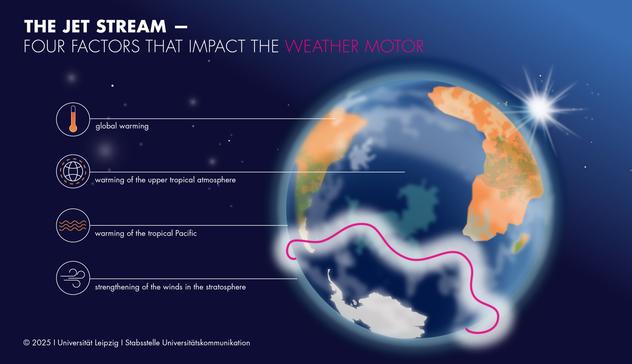
Neue Erkenntnisse über den #Jetstream ermöglichen bessere Klimavorhersagen:
Forschende der #UniLeipzig und weiterer Forschungseinrichtungen haben entschlüsselt, wie sich der #Klimawandel auf den „Wettermotor“ auswirkt.
Mehr erfahren: https://www.uni-leipzig.de/newsdetail/artikel/neue-erkenntnisse-ueber-den-jetstream-ermoeglichen-bessere-klimavorhersagen-2025-07-15
#Meteorologie #Klimaforschung #Klimakausalität
What you always wanted to know, especially in summer, but never dared to ask
about jetstream and Rossby waves,
Mike Mann has you covered.
Pub-sci article, written 2019 for the curious like you and me.
Where the curtain folds come into existence, and why – and then, what the folds do with the weather on the ground when they stay locked in place – locked for reasons also explained.
Quantum is also used!!

Why Planes Follow This Invisible Path Across the Atlantic Jet Stream Highway
The winner (as always) is #Google #Chrome, and many of the other #Chromium powered browsers like #Brave, #Vivaldi, and #Arc manage to keep up.
#Thorium doesn't, probably due to an older version of Chromium, and #Edge is still unusually slow. Edge can't even finish #JetStream.
Surprisingly #Opera has gotten especially slow, though it used to be among the fastest.
https://phys.org/news/2025-07-ocean-atmosphere-equally-responsible-atlantic.html
(like the apparent static storm front from TX to PA, and the 'Gulf formerly known to be of Mexico' turning into a steaming crock pot?)
"The cold blob can disturb the atmospheric #jetstream and storm activities, so it has implications for #extremeweather events in North America and Europe," said Laifang Li, assistant professor of #meteorology and atmospheric science at Penn State.

Is a broken jet stream causing extreme weather that lasts longer?
Scientists are scrambling to understand how climate change may be interfering with the winds that carry our weather, with potentially catastrophic consequences…
https://www.europesays.com/uk/208591/ Air India Halts Flights to Europe, U.S. East Coast, and Middle East #AirIndia #EU #Europe #European #Iran #JetStream #MiddleEast #Qatar #UnitedStates
Airlines Cancel and Divert Routes as U.S. Enters War With Iran https://www.byteseu.com/1129172/ #AmericanAirlines #BritishAirways #Conflicts #DeltaAirLines #ElAl #emirates #etihad #Iran #Israel #JetStream #MiddleEast #QatarAirways #Syria #TrumpEffect #UnitedAirlines
Strange Atlantic cold spot linked to century-long slowdown of major ocean current
The #AMOC acts like a giant conveyor belt, delivering heat and salt from the tropics to the North #Atlantic. A slowdown in this system means less warm, salty water reaches the sub-polar region, resulting in the cooling and freshening observed south of #Greenland.
When the current slows, less heat and salt reach the North Atlantic, leading to cooler, fresher surface waters. This is why salinity and temperature data can be used to understand the strength of the AMOC.
The study also found that the weakening of the AMOC correlates with decreased #salinity. This is another clear sign that less warm, salty water is being transported northward.
The consequences are broad. The South Greenland anomaly matters not just because it's unusual, but because it's one of the most sensitive regions to changes in ocean circulation. It affects #weather patterns across #Europe, altering #rainfall and shifting the #JetStream, which is a high-altitude air current that steers weather systems and helps regulate temperatures across North #America and Europe.
The slowdown may also disturb marine #EcoSystems as changes in salinity and temperature influence where species can live.
https://phys.org/news/2025-06-strange-atlantic-cold-ocean-slowdown.html
Original open acces article
Li et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (June 16, 2025) 122 (25) e2504482122
Increased frequency of planetary wave resonance events over the past half-century
#FYI #PaulBeckwith video lecture and literature review #jetstream
(Paul wearing his Solar Radiation Modifier =D)
We succeded in trashing the jet streams -.-
Paul explains, what that means
Mehr Wetterextreme durch atmosphärische Wellenstaus. Blockaden planetarer „Windautobahnen“ haben sich in den letzten 70 Jahren verdreifacht. #Wetterextrem #Extremwetter #Jetstream #Klima #Klimawandel
https://www.scinexx.de/news/geowissen/mehr-wetterextreme-durch-atmosphaerische-wellenstaus/

Rauch von Waldbränden in #Kanada hat am Wochenende für ungewöhnlich orangefarbene Himmelsphänomene über dem Vereinigten Königreich gesorgt.
Die Partikel in der #Atmosphäre streuen blaues Licht, sodass Rot- und Orangetöne dominieren. Die #Rauchwolken wurden durch den #Jetstream über den #Atlantik transportiert.

More on Bananas from North Atlantic in 2023, here by #MattEngland, Stefan #Rahmstorf et al
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08903-5
They also wrote prose on the Conversation https://theconversation.com/unprecedented-heat-in-the-north-atlantic-ocean-kickstarted-europes-hellish-2023-summer-now-we-know-what-caused-it-258061
Low surface wind speed led to shallower-than-normal ocean mixing which enabled heating the surface more.
Less clouds from shipping SO2 were only marginally responsible and only in small pockets.
Okay. But where did the wind go?
Surface wind is impacted by jetstream. And I think, the jetstream got diverted in June and July 2023 to Northern Greenland. Due to low spring snow cover in Eastern Canada which led to dry soil – which in turn gets hotter than wet soil.
And according to
"Summer atmospheric circulation over Greenland in response to Arctic amplification and diminished spring snow cover over Canada" by
Preece et al 2023
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39466-6
that hot soil in Eastern Canada leads to a High over Greenland – and a low over the #ColdBlob
East Canada was ablaze in June July 2023 suggesting dry and hence hot soil =perfect conditions for a North Greenland High, diverting the jetstream.
https://www.europesays.com/2104775/ Airlines Reshape Business Class to Fit More Seats #Airbus #Boeing #JetStream #NewZealand #PassengerExperience